Investigation
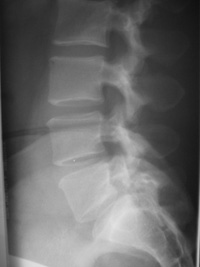
X Ray
This may be performed on the day of your appointment. The xrays will be seen by Mr Chapple and reported on after the appointment by a consultant radiologist.
Xrays give information about the bones and joints, the curves of the spine and the heights of the discs.
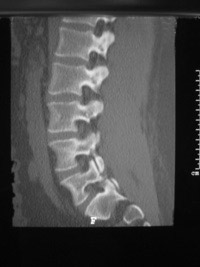
CT Scanning
CT scanning gives a three dimensional view of soft tissues, blood vessels as well as bones. It uses x-ray radiation exposure. CT scanning is booked at Salisbury Hospital NHS Trust. The scans will be seen by Mr Chapple and also reported by a consultant radiologist.
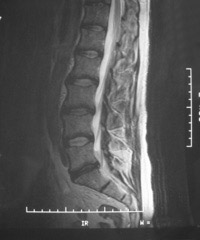
MRI Scanning
MRI scanning gives a high quality scan of all the tissues of the body. It involves the patient going into a non harmful magnetic field. This is in the form of a tunnel. As a result some patients may not be suitable to have MRI scans.
If you have claustrophobia it is possible to have an MRI scan in an open scanner and Mr Chapple can refer you for this. It is important that every patient completes the MRI safety questionnaire before they have a scan.
Bone Scanning
A bone scan looks for abnormalities in the bones. It is also known as a radionuclide scan, or a scintogram. This will be booked at the ‘Nuclear Medicine’ Department of Salisbury Hospital NHS Trust. A bone scan can look at a particular joint or bone. The scan involves having an injection of a small amount of substance called a radionuclide the amounts are non- harmful.
The scan uses a ‘gamma camera’. This is a camera that picks up signals from the radionucliotide. The radionuclide travels through the blood and collects in your bones. More of it tends to collect in areas where there is a lot of activity in the bone. These areas of activity are picked out by the camera and give a picture of your skeleton.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are occasionally used in the diagnosis of spinal problems. Blood tests can show inflammation, infection and metabolic conditions which may be contributing to the symptoms. The types of blood tests requested will be discussed with the patient.
Blood tests can be taken in outpatients at New Hall Hospital and results are normally availble in 1-2 days.
Any, clinically significant, abnormal blood tests will be discussed with the patient and their GP will be notified.
Diagnostic Injections
Injections can be used in cases where even with the MR scan or other diagnostic tests it is uncertain which area of the spine is causing the patient’s symptoms. Injections which change the patient’s symptoms can give useful diagnostic information about which level of the spine is causing the patient’s symptoms.
Indications for diagnostic injections:
Diagnostic injections can be used in
• sciatica,
• spinal stenosis,
• lateral recess stenosis,
• annular tears,
• discogenic back pain,
• neurogenic back pain,
• foraminal stenosis,
• far lateral disc protrusions
• central disc herniations
• trochanteric bursitis
• sacroiliac joint conditions
• large joint disease
Discography
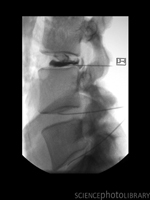 Discography may be required to determine which vertebral discs are causing the symptoms. This is an investigation done under X-ray guidance . The procedure is done as a day case.
Discography may be required to determine which vertebral discs are causing the symptoms. This is an investigation done under X-ray guidance . The procedure is done as a day case.
A contrast medium is injected into the disc space and x-ray images are taken. The procedure can be uncomfortable and for this reason is normally done with some light sedation. It is only undertaken after full discussion with the patient when the decision has been made that the benefits of the information that it will yield out way the risks. The risks of discography are small in Mr Chapple’s experience. The main risk is of infection or nerve root irritation.


